The ankle joint relies on a complex network of ligaments, tendons, and muscles to maintain stability during movement. When this delicate balance is disrupted through sudden twisting, rolling, or turning motions, the resulting injury can cause pain, swelling, and functional limitations. Proper identification and management of ankle sprains can prevent complications and reduce the risk of chronic instability.
What Is an Ankle Sprain?
An ankle sprain occurs when one or more ligaments in the ankle joint are stretched or torn. Ligaments are tough, fibrous bands of tissue that connect bones to other bones and provide stability to joints. The ankle contains three main groups of ligaments: the lateral (outer) ligaments, medial (inner) ligaments, and syndesmotic ligaments that connect the two lower leg bones.
Ankle sprains are classified into three grades based on severity. Grade I sprains involve mild stretching of the ligament with minimal tearing, Grade II sprains involve partial tearing of the ligament, and Grade III sprains involve complete rupture of the ligament. Each grade presents with different symptoms and requires varying treatment approaches.
What Causes It?
Ankle sprains typically result from sudden, unexpected movements that cause the ankle to move beyond its normal range of motion. One of the most common mechanisms is inversion, where the foot rolls inward and the ankle turns outward. This motion places excessive stress on the lateral ligaments, causing them to stretch or tear.
Running on uneven surfaces, hiking, and dancing contribute to the incidence of sprains. Non-athletic causes include walking on uneven surfaces, stepping off curbs unexpectedly, or wearing inappropriate footwear. Previous ankle injuries, muscle weakness, and proprioceptive deficits can predispose individuals to recurrent sprains.
What Are the Symptoms?
Symptoms vary depending on the severity of the injury and which ligaments are affected. Pain is typically the first and most prominent symptom, often described as sharp or stabbing at the moment of injury. The pain may initially be severe but can decrease within hours, potentially leading some individuals to underestimate the severity of the injury.
Swelling develops rapidly following the injury, typically within the first few hours. Bruising may extend beyond the immediate injury site due to gravity and the movement of tissue fluid. Functional symptoms include difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot, reduced range of motion, and instability of the foot.
How Can You Recover Quickly?
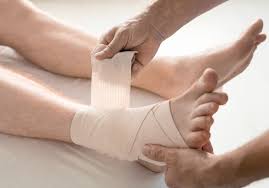
Initial treatment focuses on controlling pain and inflammation while protecting the injured ligaments from further damage. The RICE protocol (rest, ice, compression, elevation) is a cornerstone of acute ankle sprain management. Rest involves avoiding activities that cause pain and may include partial or complete weight-bearing restrictions, depending on the severity of the injury.
Ice application should begin immediately after injury. Compression using an elastic bandage or ankle brace can help control swelling and provide mild support. Elevation of the injured ankle above heart level when possible can reduce swelling by promoting fluid drainage.
Physical rehabilitation plays a valuable role in recovery and the prevention of recurrent injuries. Early mobilization within pain tolerance can promote healing and prevent excessive stiffness. Range of motion exercises should begin as soon as tolerated, progressing to strengthening and balance training as symptoms improve.
Talk to a Specialist Today
Ankle sprains require appropriate evaluation and treatment to promote healing and prevent long-term complications. Professional evaluation by a healthcare provider specializing in musculoskeletal injuries can provide an accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment recommendations, and guidance throughout the recovery process. Contact a sports medicine specialist today to discuss your sprain and develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Social Sharing
Your Content Goes Here
Latest Posts