Dental restoration encompasses various procedures designed to repair, replace, or enhance damaged or missing teeth. These treatments aim to restore proper function, improve aesthetics, and maintain oral health. Among the available options, patients often face decisions between different types of implants and restorative procedures, each offering distinct benefits depending on individual circumstances. Here’s more information on endodontic implants and other dental restoration treatments:
What Are Endodontic Implants?
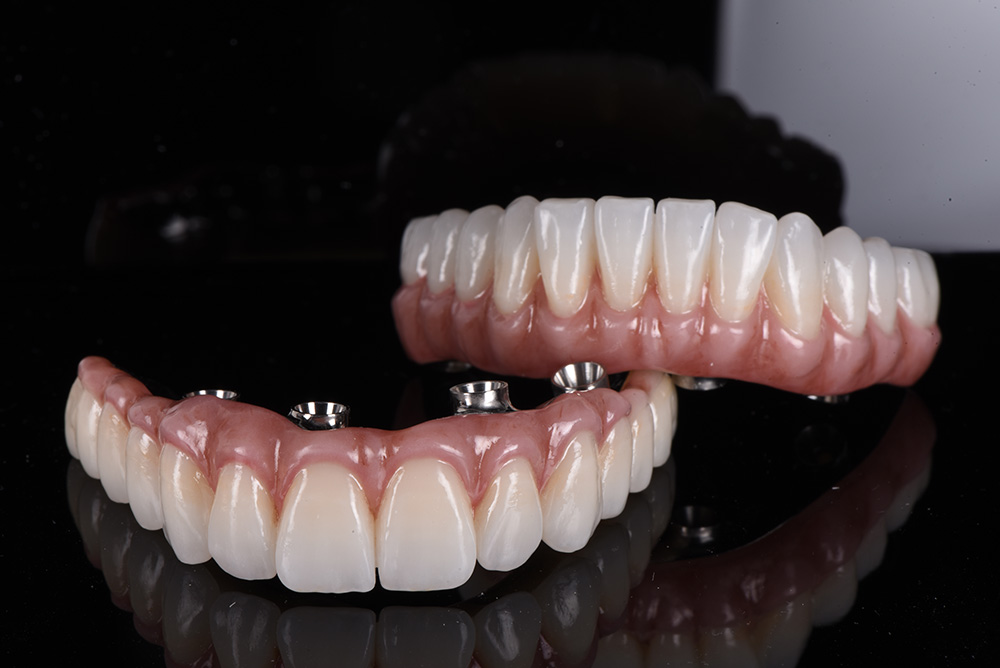
Endodontic implants are a specialized approach to tooth replacement that involves placing a titanium post directly into the jawbone. This procedure creates a stable foundation for artificial teeth by allowing the implant to integrate with the surrounding bone tissue through a process called osseointegration. An endodontic procedure typically requires several months for complete healing and integration. During this time, the titanium post fuses with the jawbone, creating a permanent anchor that can support a crown, bridge, or denture.
These implants offer exceptional stability and durability, often lasting for years with proper care and maintenance. These implants work by stimulating the jawbone, preventing the bone loss that commonly occurs after tooth loss. This stimulation helps maintain facial structure while improving oral functionality to eat and speak more easily.
How Do Endodontic and Dental Implants Differ?
While both endodontic and dental implants serve restorative purposes, they address different situations and offer unique advantages. Traditional dental implants replace entire missing teeth, including the root structure. The titanium post is surgically placed into the jawbone, and after healing, a crown is attached to complete the restoration.
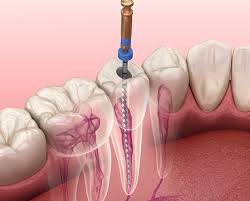
Endodontic implants focus on preserving existing tooth structures whenever possible. These procedures often involve root canal therapy combined with implant technology, allowing patients to maintain their natural teeth while addressing internal damage or infection. Endodontic implantation procedures involve adding a metal artificial root extension through the middle of the natural tooth, stabilizing it in the jaw.
The key differences of these two implantation methods lie in their different approaches to oral preservation. Dental implants require complete tooth removal, while endodontic implants work to save compromised teeth through specialized treatments. Recovery times also vary between these approaches. Traditional dental implants typically require three to nine months for osseointegration. Endodontic procedures may involve shorter healing periods depending on the complexity of the case.
When Are Endodontic Implants Necessary?
Endodontic implants become necessary when natural teeth have severe internal damage but retain sufficient healthy structure for preservation. Typical uses include teeth with extensive decay that reaches the pulp, fractured roots, or persistent infections that haven’t responded to conventional treatments. These procedures prove particularly beneficial for patients who want to avoid extraction and maintain their natural tooth structure.
Who Is a Good Candidate?
Candidates for endodontic implants typically have adequate bone density and healthy gums to support the procedure. Age, overall health, and commitment to proper oral hygiene also influence treatment suitability. Patients with certain medical conditions or those taking specific medications may require additional evaluation before proceeding.
What Are Some Other Restorative Options?
The decision between endodontic implants and other restoration options depends on factors like the extent of tooth damage, bone quality, patient preferences, and long-term oral health goals. Professional evaluation helps determine the most appropriate treatment approach for each individual situation. Some other restoration procedure options are:
- Dental Crowns: Designed to restore the shape, strength, and function of a heavily damaged or decayed tooth.
- Dental Bridges: Used to replace one or more missing teeth by anchoring to adjacent healthy teeth.
- Dentures: Removable prosthetics that replace multiple missing teeth, either partially or entirely.
- Veneers: Thin coverings placed over the front side of the teeth to enhance appearance and address cosmetic imperfections.
Schedule an Appointment Today
Dental restorations can repair teeth and restore function to your mouth. Qualified dental professionals can evaluate the condition of your teeth and help you make informed decisions about your oral health care. Contact a qualified dental practice to schedule your consultation and explore how restorative procedures might benefit your oral health.
Social Sharing
Your Content Goes Here
Latest Posts